
HORSE SHOE CRAB BLOOD
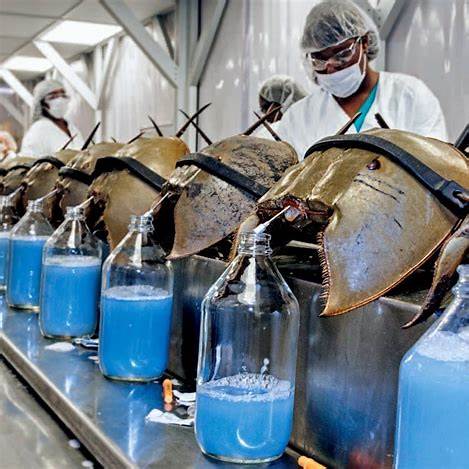

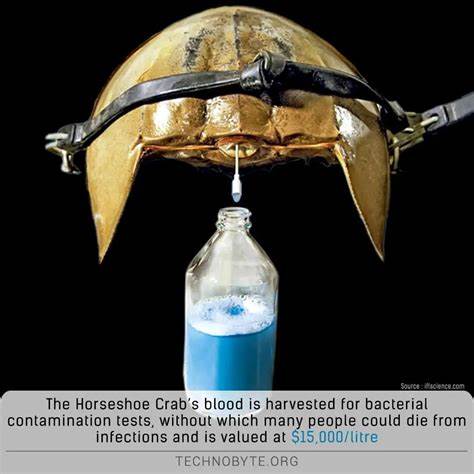


Horseshoe crab blood is a unique and valuable component in the medical industry, primarily due to its ability to detect bacterial endotoxins.
Composition and Characteristics:
Color and Composition: The blood of horseshoe crabs is blue because it contains hemocyanin, a copper-based molecule that transports oxygen.
Amebocytes: These blood cells play a crucial role in the animal’s immune response by detecting and responding to pathogens.
Medical Uses:
Limulus Amebocyte Lysate (LAL) Test: Extracted amebocytes are used to produce LAL, a reagent essential for testing bacterial endotoxins in medical applications. This test ensures the safety of various medical products, including vaccines, intravenous drugs, surgical implants, and prosthetics.
Recombinant Factor C (rFC) Assay: Developed as a synthetic alternative, rFC utilizes a protein from horseshoe crab blood to detect endotoxins. While it offers a synthetic option, its adoption varies, and horseshoe crabs remain a primary source for endotoxin testing.
Conservation Concerns:
The demand for horseshoe crab blood has raised environmental and ethical concerns. The collection process can lead to significant mortality rates, with estimates ranging from 10% to 30%. Additionally, the practice may impact the crabs’ ability to spawn, affecting their populations.
In summary, horseshoe crab blood is indispensable in ensuring the safety of medical products through endotoxin testing. However, ongoing efforts are essential to develop alternative methods and sustainable practices to mitigate the impact on horseshoe crab populations.
